基础数据类型
- Point 坐标类
Point有两种,2维Point和3维Point,Point可以转换为其他数据类型,比如vector或者matrix
- Scala
Scalar继承于vector
Scalar(b, g, r) :b->蓝色分量 g->绿色分量 r->红色分量
Scalar(0, 0, 255) -> 红色像素点
- Size 大小类
Size和Point类似,两者可以互相转换,不同之处在于Point的数据成员名为x和y,Size的数据成员名为width和height
- Rect 矩形类
Rect成员包含Point类型的x,y和Size类型的width,height
- RotatedRect 旋转矩形类
RotatedRect包含中心点(Point),大小(Size),旋转角度
- InputArray OutputArray
InputArray和OutputArray区别在于 InputArray为只读,上述基础数据类型都可转换为 InputArray或OutputArray,以此保持函数的简洁性工具函数
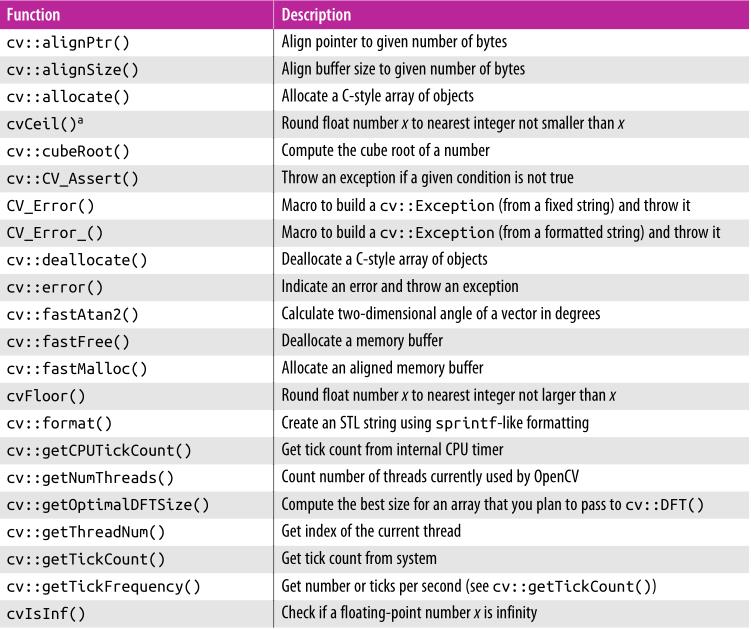

- cv::alignPtr() 指针对齐
// Return aligned pointer of type T* template<T> T* cv::alignPtr( T* ptr, // pointer, unaligned int n = sizeof(T)); // align to block size, a power of 2 - cv::allocate() 分配具有T类型的对象数组(C风格)
// Return pointer to allocated buffer template<T> T* cv::allocate( size_t sz); // buffer size, multiples of sizeof(T) - cv::fastAtan2() 计算向量方向 x(向量的x坐标) y(向量的y坐标)
float cv::fastAtan2(float y, float x ); - cvCeil() 返回不小于x的最小整数值
int cvCeil(float x); - cvRound() 返回与x最接近的整数值
int cvRound( double x ); - cvFloor() 返回不大于x的最大整数值
int cvFloor( float x}; - cv::cubeRoot() 计算x的立方根
float cv::cubeRoot( float x); - cv::format() 格式化输出
string cv::format(const char* fmt, ... );
帮助类
- TermCriteria 算法终止条件类
TermCriteria( int type, int maxCount, double epsilon) 类型 迭代次数 超参数 - Range 整数序列
Range(0,4) —-> 0,1,2,3
Mat N维稠密矩阵
构造矩阵
Mat();
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type);
Mat(Size size, int type);
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s);
Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s);
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type);
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s);
Mat(const Mat& m);
Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi);
Mat(const Mat& m, const Range* ranges);
int rows, int cols:二维矩阵的行列数 ->图像分辨率
int type:存储元素的数据类型和通道数 CV_[位数][是否带符号][类型前缀]C[通道数]
const Scalar& s:矩阵每个元素以s向量(颜色)填充 向量维度由通道数决定
Mat matrix(2, 2, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0, 0, 255));
Mat matrix(2, 2, CV_8UC2, Scalar(1,2));
matrix = [ 0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255 ; 0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255]
matrix = [ 1, 2, 1, 2 ; 1, 2, 1, 2]
Mat m;
m.create(3,10,CV_32FC3)
m.setTo(Scalar(1.0f,1.0f,1.0f));//设置第一个通道的值
Mat matrix = Mat::eye(4, 4, CV_64F);
Mat matrix = Mat::ones(4, 4, CV_32F);
Mat matrix = Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_8SC1);
[1, 0, 0, 0;
0, 1, 0, 0;
0, 0, 1, 0;
0, 0, 0, 1]
[1, 1, 1, 1;
1, 1, 1, 1;
1, 1, 1, 1;
1, 1, 1, 1]
[ 0, 0, 0;
0, 0, 0;
0, 0, 0]
Mat matrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9);
[1, 2, 3;
4, 5, 6;
7, 8, 9]
利用clone() 或者 copyTo()
Mat RowClone = matrix.row(1).clone();
cout << "RowClone = " << endl << " " << RowClone << endl << endl;
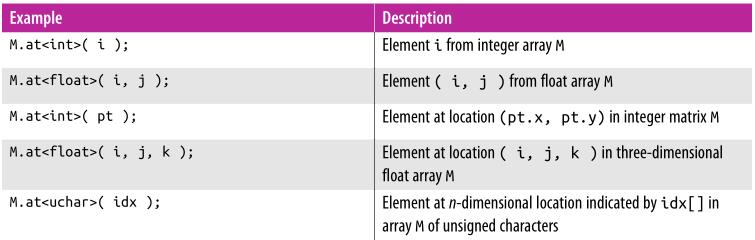
获取矩阵元素
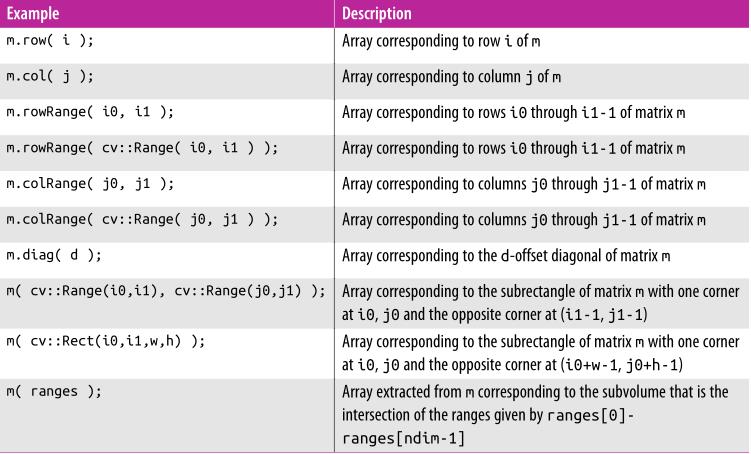
矩阵运算
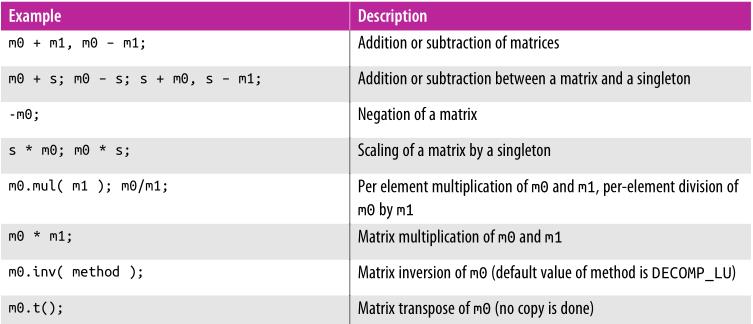
矩阵操作
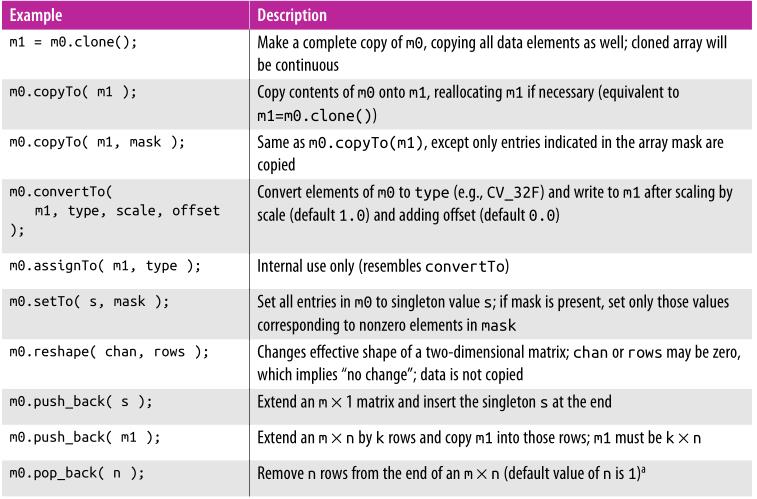
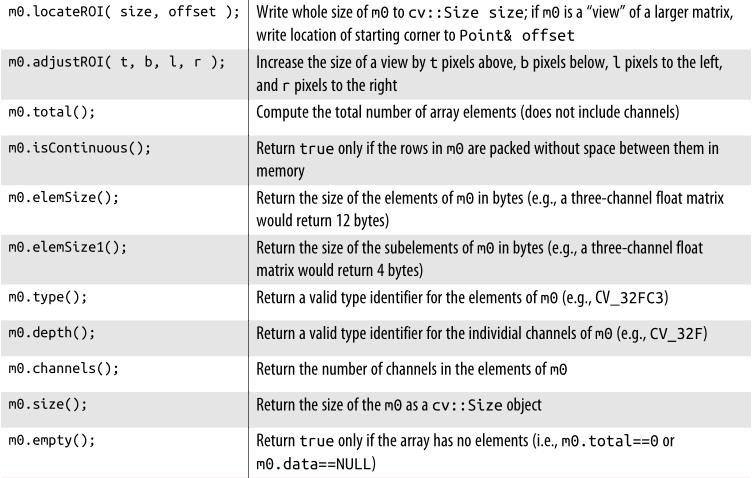
打印矩阵
Mat matrix(2,2, CV_8UC3, Scalar(0,0,255));
默认风格
std::cout << matrix << std::endl;
[ 0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255;
0, 0, 255, 0, 0, 255]
Python风格
std::cout << format(matrix,Formatter::FMT_PYTHON) << std::endl;
[[[ 0, 0, 255],
[ 0, 0, 255]],
[[ 0, 0, 255],
[ 0, 0, 255]]]
Numpy风格
std::cout << format(matrix, Formatter::FMT_NUMPY) << std::endl;
array([[[ 0, 0, 255], [ 0, 0, 255], [ 0, 0, 255]],
[[ 0, 0, 255], [ 0, 0, 255], [ 0, 0, 255]],
[[ 0, 0, 255], [ 0, 0, 255], [ 0, 0, 255]]], dtype=’uint8’)
版权声明:原创,转载请注明来源,否则律师函警告
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 3.0协议 。转载请注明出处!